WWII in Europe, 1939-45
German victories, 1939-42
1.Hitler defeated Poland in five
weeks using blitzkrieg tactics. Germany & the Soviet Union divided Poland
between them.
1.After this attack,
there was no fighting during the winter of 1939-40 in what people called the
Phoney War; both sides built up their weapons.
Blitzkrieg
2.Next Hitler conquered Denmark
& Norway.
1.He wanted Norway to
protect the supply route of iron ore, which came from Sweden during the winter;
this was vital for his war industries.
3. Then Hitler attacked Belgium,
Holland & France. Hitler used blitzkrieg tactics & cut off the British
& French armies at Dunkirk in France.
Operation Dynamo = British sent over 100’s of boats to rescue thousands
of soldiers from the beaches of Dunkirk.
Hitler easily captured the Maginot Line (a French defensive line); then he divided France,
ruling part of it directly, the other part ruled as Vichy France under German control.
Operation Dynamo
 |
| Maginot Line |
4. Churchill organised British
resistance to Hitler in the Battle of Britain.
Hitler’s plan to invade Britain was called Operation Sea
Lion. First he had to control the air over the English Channel. The RAF &
Luftwaffe fought for control of the air in the Battle of Britain.
Britain defeated the Germans with the help of radar,
which told them where the Germans were going to attack.
British use of Radar in WW2
5. The Battle of Britain was
followed by the Blitz – the Luftwaffe attack on British cities over the winter
of 1940/41.
Cities such as London & Coventry were attacked; some
people evacuated to the countryside, but many stayed in the cities.
London people slept in the Underground.
The Blitz ended when Hitler ordered the attack on Soviet
Russia.
The Battle of Britain
Battle of Britain Newsreel
The Blitz
The Blitz: Experience of a Boy
6. Operation Barbarossa - invasion of the Soviet Union. Hitler attacked
Russia because he hated communists & he wanted Lebensraum.
He attacked towards Leningrad, Moscow & Kiev with
Blitzkrieg tactics.
Stalin encouraged the people to fight in
what the Russians called the Great Patriotic War. He ordered the
industries be moved behind the Ural Mountains, away from German attack. He
ordered a scorched-earth
policy of destroying all crops so that the
Germans could not use them as they advanced.
The Germans’ advance was halted by the winter snow.
Operation Barbarossa
People in History- A German soldier in Operation Barbarossa
Battle of Stalingrad: In the following year, Hitler ordered an attack on
Stalingrad; there was vicious street
fighting & the German army was trapped in Stalingrad; 200,000 German
soldiers had to surrender; this was a major turning point in the war.
Battle of Stalingrad - Enemy at the Gates
7. USA joined the war
when Japan attacked Pearl Harbour in December 1941; America became the arsenal of democracy, supplying Britain with food & weapons.
Pearl Harbour
8. The War at Sea:
Britain and USA won the war at sea (AKA Battle of the Atlantic),
a battle against German U-boats as they attacked convoys bringing supplies to
Britain; the Allies won because of increased shipbuilding & use of Ultra,
which cracked the German codes sending messages to their submarines.
Enigma - Breaking of German codes
9. The War in the Air:
Britain & USA bombed Germany by day & night, e.g. Hamburg; 30,000 people were killed on a raid in Dresden.
Germans counter-attacked by using V1 flying bombs & V2 rockets against Britain.
Dresden Raid
V1 Flying Bomb
V2 Rocket
The Allies advance, 1942-45
10. The Allies advance from the
south through Italy; Mussolini
was deposed by the Italians & he was
captured & shot; body hung in Milan.
11. Soviet Union advanced from
the east.
12. D-Day, Operation Overlord: the Allies planned a landing on the coast of Normandy
in France. They used the coastline’s shallow water, sandy beaches &
proximity to England to surprise the Germans.
General Eishenhower commanded the Allied forces; Allied planes bombed the
German defences of the Atlantic Wall; paratroopers dropped behind enemy lines;
warships & landing craft landed American, British & Canadian troops on
five beaches (Omaha, Utah, Gold, Juno & Sword).
 |
| General Eishenhower |
Allies built PLUTO (Pipeline under the ocean) to supply
oil & Mulberry Harbours (floating artificial piers) in order to land trucks
& tanks.
They advanced on Paris.
D-Day Landings - Saving Private Ryan
D-Day original footage
|Eishenhower Speech D-Day
13. Hitler’s suicide: Hitler committed suicide in his bunker in Berlin as
the Allied armies closed in on Berlin. Germany surrendered.
BBC Broadcast Hitler Is Dead
Why did the Allies win the war?
1.Allies had a larger population
& larger armies than Germany, Italy & others.
2.USA produced huge numbers of
tanks, planes & weapons to keep the Allies going through the war.
3.The Allies produced more oil than
the Germans.
4.Allies won the major battles of
the war – Battle of Britain, Stalingrad, D-Day.
What were the results of WW2?
1.55 million people, civilians
& soldiers, died.
2.Cities, industries, roads &
railways destroyed.
3.Nazi war criminals such as
Goering tired in the Nuremberg
Trials.
Nuremberg Trials
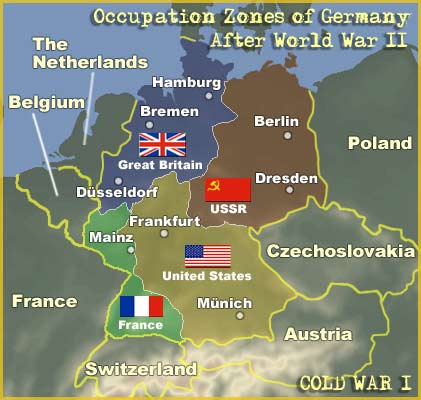
4.As agreed at the Yalta Conference
between Roosevelt, Churchill & Stalin, Germany was divided in two between the Soviet-controlled East Germany &
Allied-controlled West Germany. The two were re-united when communism collapsed
in 1990.
5. Relations between USA &
Soviet Union worsened & turned into the Cold War after WWII was
over; the Soviet Union installed communist governments in Eastern European
states.
6. The USA & Soviet Union
became the Superpowers and Europe was weakened.
7. European leaders began to
drive to European unity after the war.
Atomic BombReview Questions
48. What was meant by a ‘blitzkrieg’ war?
49. What happened at Dunkirk?
50. What happened to France during World War Two?
51. What was the Battle of Britain?
52. What happened during the Blitz?
53. What was ‘Operation Barbarossa’ and what were the main consequences?
54. Why did the USA enter WWII?
55. What was D-Day?
56. Who were the main Allied military commanders in WWII?
57. Who were the main German commanders in WWII?
58. What brought WWII to a final end?
59. How was WWII different from all previous wars?
60. What were the Nuremberg trials?
Answers
48. This was a new type of war. First planes attacked and bombed targets. Then tanks were sent in. And finally large numbers of troops on trucks moved in to take control. This was first used in Poland by the Germans.
49. Large numbers of French and British troops were completely surrounded by the German army. They were forced to evacuate from the port of Dunkirk. Every available boat was sent over from Britain to do this.
50. All of northern and western France came completely under German control. Hitler walked in victory under the Arc de Triomphe in Paris. The Southeast of France had a government of its own. It was called Vichy France because it was based in the town of Vichy. It was very pro-German.
51. This was when the German airforce attacked Britain. Battles took place between the Luftwaffe and the RAF. Both sides suffered huge losses. However Britain had the great advantage of radar.
52. This was when Hitler decided to change his tactics. Instead of attacking the RAF, the Luftwaffe bombed British cities every night for nearly six months. Huge damage was caused and thousands were killed. Worst hit were London and Coventry.
53. This was the German attack on the USSR in the summer of 1941.
54. Because Japan attacked their main naval base at Pearl harbour. Japan was on the side of Germany in WW2.
55. This was when the Allies launched a massive beach landing of troops in Normandy in France in June 1944. They then began to drive the Germans out of France.
56. General Montgomery and General Eisenhower.
57. General Rommel.
58. When the USA dropped 2 atomic bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in august 1945. Over 100,000 people were killed instantly. Japan then surrendered and this was the end of WW2.
59. Millions more died, blitzkrieg war used, millions of civilians died, atomic bombs used for first time.
60. This was when the leaders of Nazi Germany were put on trial at the end of WW2.
49. What happened at Dunkirk?
50. What happened to France during World War Two?
51. What was the Battle of Britain?
52. What happened during the Blitz?
53. What was ‘Operation Barbarossa’ and what were the main consequences?
54. Why did the USA enter WWII?
55. What was D-Day?
56. Who were the main Allied military commanders in WWII?
57. Who were the main German commanders in WWII?
58. What brought WWII to a final end?
59. How was WWII different from all previous wars?
60. What were the Nuremberg trials?
Answers
48. This was a new type of war. First planes attacked and bombed targets. Then tanks were sent in. And finally large numbers of troops on trucks moved in to take control. This was first used in Poland by the Germans.
49. Large numbers of French and British troops were completely surrounded by the German army. They were forced to evacuate from the port of Dunkirk. Every available boat was sent over from Britain to do this.
50. All of northern and western France came completely under German control. Hitler walked in victory under the Arc de Triomphe in Paris. The Southeast of France had a government of its own. It was called Vichy France because it was based in the town of Vichy. It was very pro-German.
51. This was when the German airforce attacked Britain. Battles took place between the Luftwaffe and the RAF. Both sides suffered huge losses. However Britain had the great advantage of radar.
52. This was when Hitler decided to change his tactics. Instead of attacking the RAF, the Luftwaffe bombed British cities every night for nearly six months. Huge damage was caused and thousands were killed. Worst hit were London and Coventry.
53. This was the German attack on the USSR in the summer of 1941.
54. Because Japan attacked their main naval base at Pearl harbour. Japan was on the side of Germany in WW2.
55. This was when the Allies launched a massive beach landing of troops in Normandy in France in June 1944. They then began to drive the Germans out of France.
56. General Montgomery and General Eisenhower.
57. General Rommel.
58. When the USA dropped 2 atomic bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in august 1945. Over 100,000 people were killed instantly. Japan then surrendered and this was the end of WW2.
59. Millions more died, blitzkrieg war used, millions of civilians died, atomic bombs used for first time.
60. This was when the leaders of Nazi Germany were put on trial at the end of WW2.
World War II – Key
terms
Blitzkreig: lightning war – (1) German
bombers destroy enemy targets. (2) Then large numbers of tanks smash through
enemy defences. (3) Infantry (foot
soldiers) advance to occupy and control newly captured territory.
Phoney War: the period between the
invasion of Poland, Oct 1939 and the invasion of Denmark, April 1940, when
enemy troops faced each other across the French – German border but didn’t
fight.
Maginot Line: Forts built along the
French German border by the French in the 1930s to protect against a German
invasion. The German forces by passed the Maginot Line and invaded France
through Belgium.
Dunkirk (Operation Dynamo): the
evacuation of 300,000 British and French troops from France. The British used
over 900 boats (warships to fishing boats) to rescue the troops from the
beaches.
The Luftwaffe: the German Air force
The Blitz: the German bombing of
British cities. During the Blitz, highly explosive bombs rained down on urban
areas. About 60,000 people died and ninety per cent of London buildings were
damaged. Hitler failed to break the morale of the British people. People spent
their nights in Underground for safety. A loud air raid siren would warn of an
attack. Children were evacuated to the countryside. Everyone was given a gas
mask in case of chemical warfare. People had to cover their windows so that no
light could be seen outside (blackout).
Battle of Kursk: the biggest tank
battle in history. Soviet tanks defeated the German tanks.
Battle of El Alamein: Another major
turning point in WWII. Italy’s efforts to extend its empire in North Africa
came unstuck, forcing Hitler to send General Rommel to Africa to rescue the
struggling Italians. The goal was to gain control of the Suez Canal. Rommel’s
forces were initially successful but they were eventually defeated by
Montgomery at the decisive battle of El Alamein in Egypt. In May 1943 the
Germans and the Italians in North Africa surrendered.
Pearl Harbour December 7th 1941:
On this day Germany’s ally Japan attacked the US Pacific fleet at pearl Harbour
in Hawaii. Japan wanted to build an empire in Asia and wanted to wipe out the
US Navy in the Pacific. 18 US ships were sunk, 200 aircraft destroyed and 2,500
men killed. The US entered the war against Japan and Germany.
Allies: America, Great Britain, Soviet
Union among others.
Axis Powers: Germany, Italy and Japan.
The Battle of the Atlantic: German
U-boats (submarines) attacked and sank hundreds of Allied cargo ships in the
Atlantic. To protect themselves, cargo ships travelled in large groups called
convoys, flanked by warships. The Allies were eventually able to defeat the
U-boat threat by: increasing shipbuilding, using air reconnaissance, radar,
sonar and by code breaking that deciphered messages sent to U-boats at sea.
The Battle of Midway Island June 1942:
the turning point in the war in the Pacific. The US Navy sank four Japanese
aircraft carriers. After this battle the US invaded a large number of Japanese
held islands in the Pacific and drove the Japanese back towards Japan.
V1 and V2: the V1 was a flying bomb and
the V2 was a rocket built by the Germans to bomb British cities. They came into
use to late in the war to effect the result.
Operation Overlord: the Allied (GB, USA
and CAN) invasion of France on 6th June 1944.
The fall of Berlin: By April 1945 the
Germans had been defeated on both fronts. Hitler called on young and old to
defend Berlin. In March 1945 the Allies crossed the Rhine and on the 30th
April 1945, Hitler committed suicide with the Soviet troops a few hundred
metres away. A week later Germany surrendered and the war in Europe was over.
Atomic bombs: the war against Japan
continued in Asia. In August 1945, to prevent having to invade Japan, US
President Harry Truman took the decision to drop an atomic bomb on Hiroshima
and Nagasaki. Both cities were destroyed. Over 100,000 people were killed and
many more in the years after for radiation. Japan surrendered soon after.
Why did the Allies win the war?
1.
The Allies had larger populations and larger
armies than the Axis Powers.
2.
American industrial might. America produced
thousands of planes, tanks, jeeps, ships for the Allied war effort. In
factories that were far away from German or Japanese bombers.
3.
Access to oil. The Allies had greater access to
oil than Hitler or the Japanese.
4.
The Allies won the key battles that were turning
points in the war – the Battle of Britain, the Battle of El Alamein and the
Battle of Stalingrad.
5.
Hitler’s invasion of Russia turned out to be a
fatal mistake for Germany.
6.
The Allied bombing of German cities and
factories reduced the military equipment Germany could build. It also meant
that the Luftwaffe was tied down defending Germany rather than winning battles.
Revison World War 2 - Kahoot
Revision WW2 - Kahoot

No comments:
Post a Comment